The intricacy and power requirements of your setup will determine whether or not your automobile audio system needs a battery isolator. A battery isolator might be quite helpful if you have a powerful vehicle audio system or intend to add more batteries to support it.
 What is a Battery Isolator?
What is a Battery Isolator?
You can use dual battery setup for car audio while keeping them apart thanks to a gadget called a battery isolator. This makes sure that when you use accessories, like a strong car music system, your vehicle’s primary battery, which starts the car, doesn’t run out of power.
Three Main Reasons Why You Need a Battery Isolator for Car Audio:
- Prevents Battery Drain: If your car’s primary battery is being used excessively by your music system, it may soon run out of juice, especially if the engine is off. By directing power consumption to a secondary battery, a car audio battery isolator makes sure that your primary battery has adequate charge to start your car.
- Effective Power Management: A battery isolator car audio assists in distributing the electrical load for those who own huge subwoofers, amplifiers, or other high-powered music equipment. It guarantees that the primary and secondary batteries receive the proper amount of charge without placing undue stress on them.
- Safety and Convenience: You run the danger of depleting the primary battery in your car and becoming stranded if you don’t have an car audio battery isolator. By dividing the two power sources, the isolator removes this issue, allowing you to enjoy your stereo system without worrying about the car starting up.
When Do You Need Battery Isolator for Car Audio?
 You probably don’t need a battery isolator if your audio system uses a reasonable amount of power and you don’t intend to use it for extended periods of time with the engine off. To safeguard your batteries and guarantee dependable operation, a second battery kit for car audio is strongly advised if you have a high-performance system or utilize it when the car is not running.
You probably don’t need a battery isolator if your audio system uses a reasonable amount of power and you don’t intend to use it for extended periods of time with the engine off. To safeguard your batteries and guarantee dependable operation, a second battery kit for car audio is strongly advised if you have a high-performance system or utilize it when the car is not running.
How to hook up a second battery for car audio?
To install a car audio second battery kit, connect the second battery in series with the main battery using high-gauge power cables. Use a battery isolator between the two batteries to prevent the audio system from draining the main battery. Run a power wire from the batteries to the isolator, then from the isolator to the second battery. Ground the second battery, and connect the audio system’s power wires to the second battery for extra power supply.
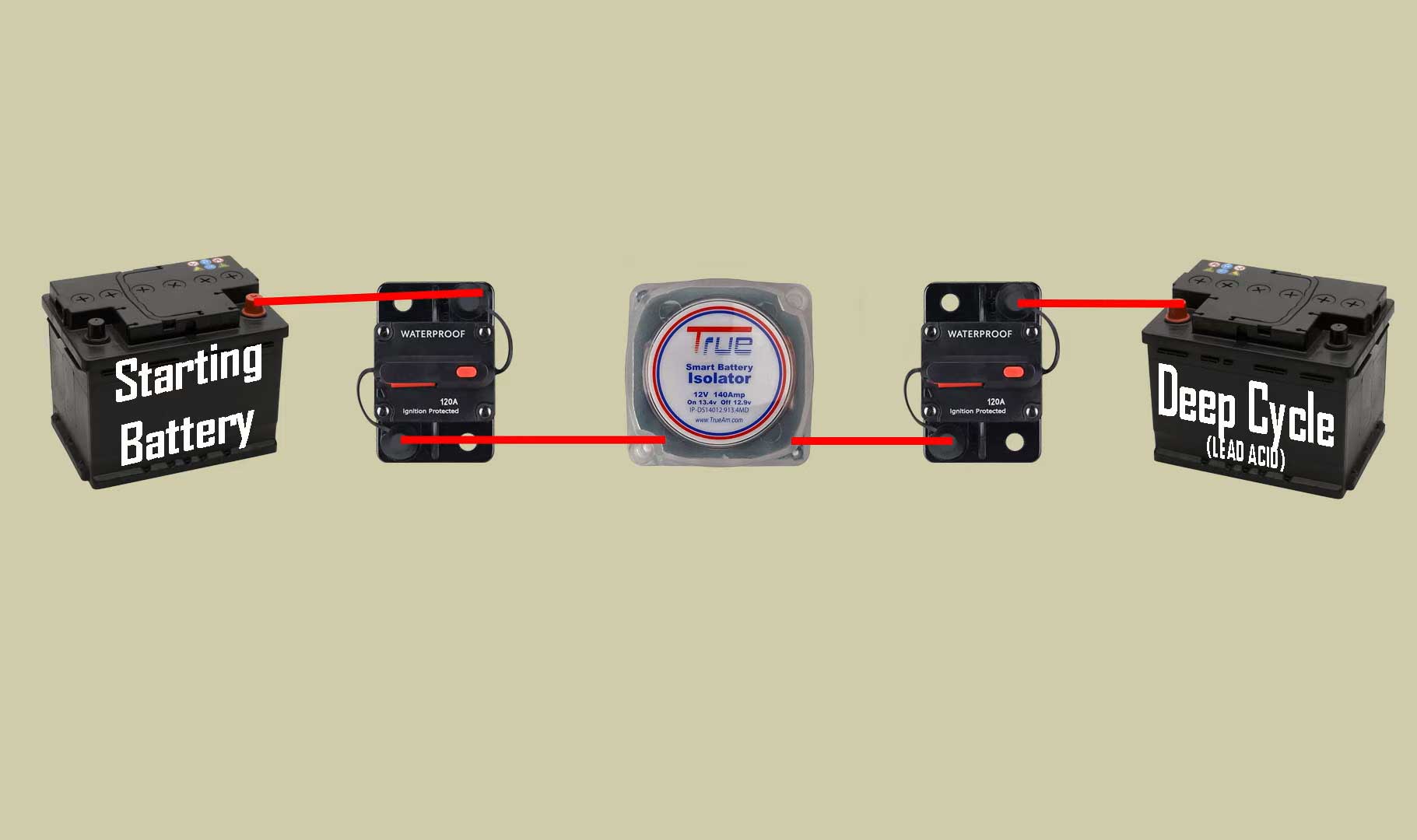
Dual battery connection diagram
A car dual battery isolator wiring involves connecting the main battery’s positive terminal to the isolator’s input, the isolator’s output to the second battery’s positive terminal, and grounding both batteries. Connect the starting battery to the isolator input, while the second battery powers the car audio system.
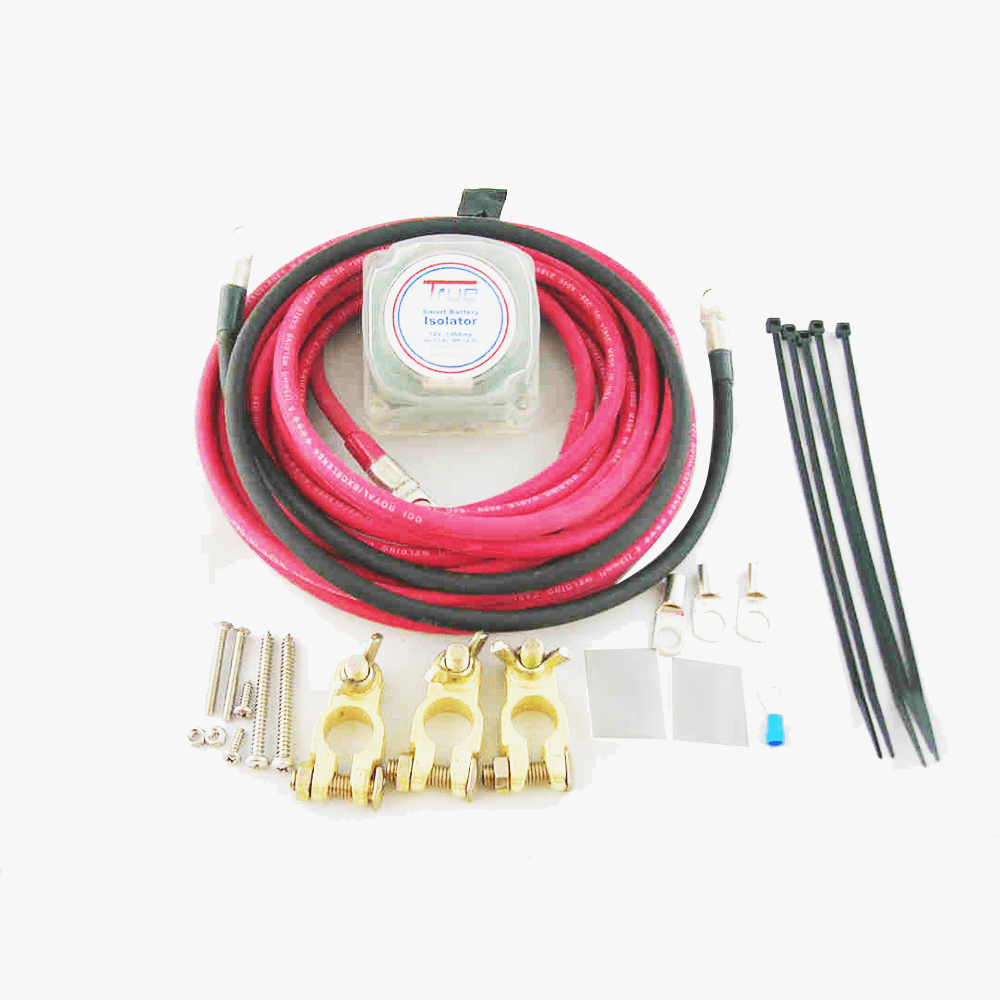
What are the basic components of a car audio second battery kit

Typically, a car audio second battery kit has all the parts needed to provide high-performance audio systems additional power. These parts include:
- heavy-gauge power cables to link the batteries and isolator,
- a battery isolator to keep the primary battery from being completely depleted, and
- a deep cycle backup battery to manage prolonged power demand. To safeguard the system against power surges, the kit may also include
- optional fuses and fuse holders,
- grounding cables for appropriate electrical grounding, and
- battery terminals for safe connections to the battery posts.
When combined, these parts provide a steady and dependable power source for the audio system in your vehicle.
Is the battery isolator maintenance free?
The majority of battery isolators do not require maintenance. They usually don’t need any further service or modifications after they’re installed. They operate automatically, splitting the alternator’s power to charge the primary and secondary batteries independently so that none drains the other.
To maintain optimal performance, it’s crucial to make sure that the wiring and connections are firmly positioned and to routinely inspect the cables and terminals for any indications of wear or corrosion. However, there is usually no need for special maintenance on the isolator itself.









