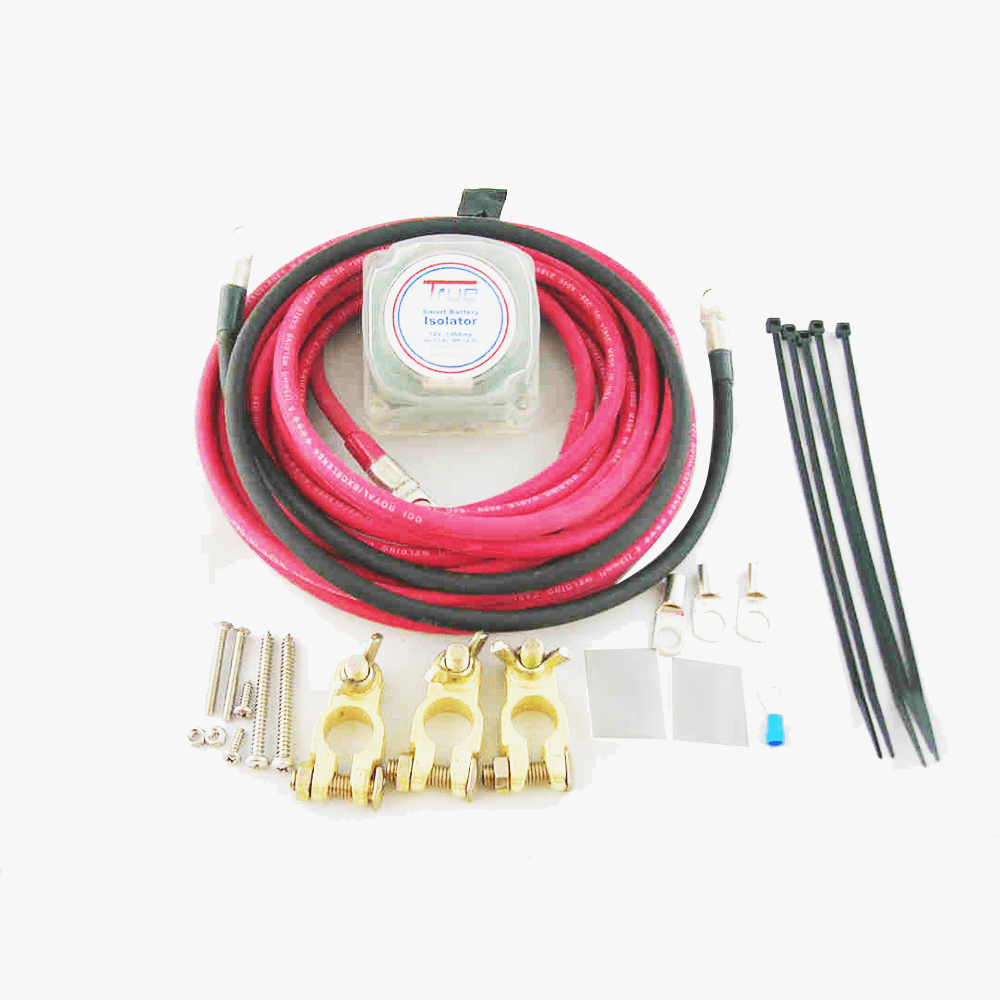
Battery isolators are essential components in dual battery systems, particularly in vehicles with high power demands or those used for off-road, camping, or heavy-duty applications.
Here’s a detailed look at the pros and cons of different types of battery isolators:
Diode Battery Isolators
Pros:
- Simplicity: Diode isolators are straightforward devices with no moving parts, making them reliable and durable.
- Maintenance-Free: They require little to no maintenance once installed.
- Protection: Effectively prevent the auxiliary battery from draining the main battery, ensuring the starting battery remains charged.
Cons:
- Voltage Drop: Diode isolators cause a slight voltage drop (typically around 0.7 volts), which can reduce charging efficiency and result in slightly lower battery charge levels.
- Heat Generation: The diodes can generate heat, requiring proper ventilation or heat sinks to dissipate the heat effectively.
Solenoid (Relay) Battery Isolators
Pros:
- No Voltage Drop: Unlike diode isolators, solenoid isolators do not cause a voltage drop, allowing the alternator’s full output to charge the batteries.
- High Current Capacity: They can handle high current loads, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- Cost-Effective: Typically less expensive than advanced isolators like VSRs.

Cons:
- Mechanical Wear: The moving parts in solenoid isolators can wear out over time, potentially leading to failure.
- Complex Installation: Installation can be more complex due to the need for a control circuit to activate the solenoid.
- Manual Operation: Some solenoid isolators require manual switching, which can be inconvenient.
Voltage-Sensitive Relays (VSR)
Pros:
- Automatic Operation: VSRs automatically connect and disconnect batteries based on voltage levels, eliminating the need for manual intervention.
- Efficiency: They ensure optimal charging of both batteries without the voltage drop associated with diode isolators.
- Ease of Use: VSRs are user-friendly, as they handle battery management automatically.
Cons:
- Cost: VSRs are typically more expensive than basic solenoid isolators or diode isolators.
- Complexity: Slightly more complex than solenoid or diode isolators, potentially requiring professional installation.
- Compatibility Issues: Not all VSRs are compatible with every vehicle or battery type, so careful selection is needed.
General Pros and Cons of Using Battery Isolators
Pros:
- Extended Battery Life: By preventing deep discharges and managing charge cycles effectively, battery isolators can extend the lifespan of your batteries.
- Increased Reliability: Ensures that your main battery remains charged and ready to start the vehicle, reducing the risk of being stranded with a dead battery.
- Power Management: Allows you to run additional electrical accessories without compromising the starting power of your vehicle.
Cons:
- Installation Complexity: Depending on the type of isolator, installation can be complex and may require professional assistance.
- Cost: There is an upfront cost associated with purchasing and installing a battery isolator, which can vary based on the type and brand.
- Space Requirements: Installing a dual battery system with an isolator requires additional space under the hood or in the vehicle, which can be a constraint in some setups.
In summary, choosing the right battery isolator depends on your specific needs, budget, and technical requirements. Diode isolators offer simplicity and reliability but suffer from voltage drop. Solenoid isolators are cost-effective and efficient but may require manual operation and are prone to mechanical wear. VSRs provide automatic, efficient operation at a higher cost and with potentially more complex installation.
Related Topics:
- Why 12V Battery Isolator Relay is Better than Diode Isolator?
- How does a voltage sensitive relay work?
- The Modern Solution to Avoid Drained Batteries
- How to wire battery isolator?
(Visited 323 times, 1 visits today)