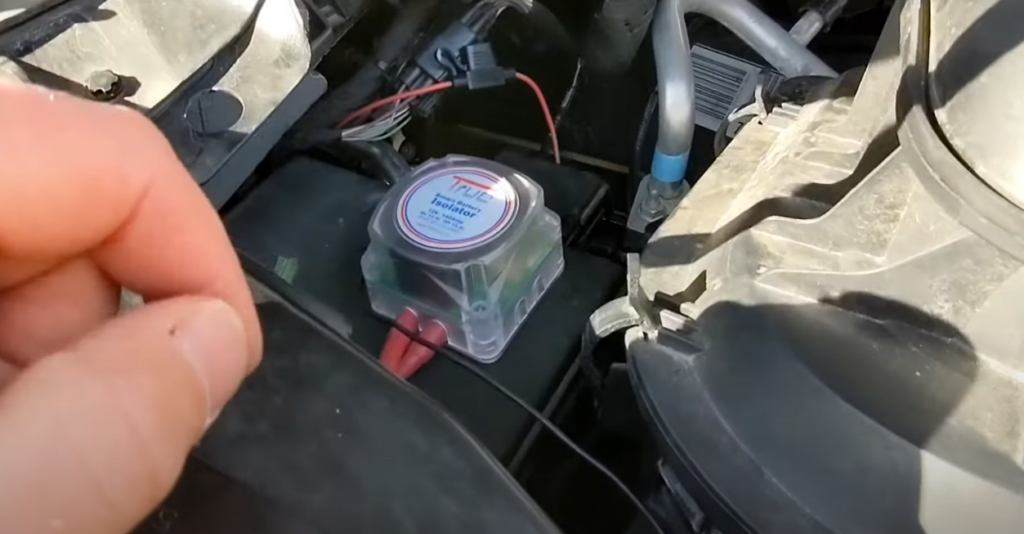
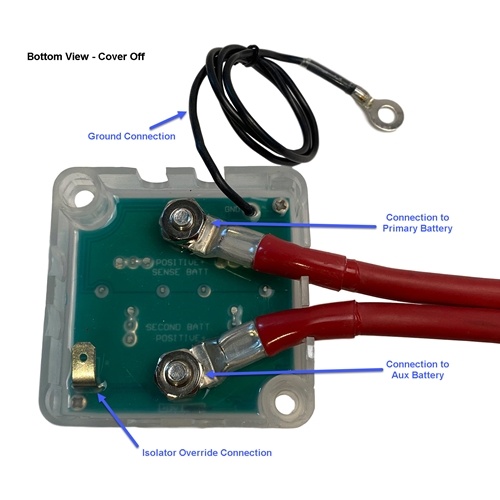
A battery isolator relay is an electrical device used in automotive and marine applications to manage multiple batteries or battery banks. Its primary function is to prevent the batteries from discharging into each other when they are connected in parallel or series.
Battery isolator relays are commonly used in applications such as recreational vehicles (RVs), boats, off-road vehicles, emergency vehicles, and other situations where multiple batteries are used to power various accessories or to provide backup power. They help maintain the integrity of each battery, extending their lifespan and ensuring reliable power distribution.
This helps ensure that you always have a reliable source of power and that one battery doesn’t drain the others, which could leave you stranded with a dead battery.
Here are some key features and functions of a battery isolator relay:
- Isolation: A battery isolator relay isolates multiple batteries from each other when the engine is not running. This means that the batteries are electrically separated, and their charge/discharge cycles do not affect one another.
- Charging: When the engine is running and the alternator is producing electricity, the battery isolator relay connects all the batteries in parallel, allowing them to charge simultaneously. This ensures that all batteries receive an equal charge.
- Voltage Sensing: Many modern battery isolator relays have voltage-sensing capabilities. They can automatically detect when the primary battery (the one connected to the vehicle’s starting system) is receiving a charge from the alternator. When the voltage reaches a certain threshold, the relay engages, connecting all batteries for charging.
- Disconnection: When the engine is turned off or the voltage drops below a certain level, the battery isolator relay disconnects the batteries from each other to prevent them from discharging into one another. This helps ensure that the primary starting battery remains charged and ready to start the engine.
Voltage-sensitive relays are commonly used in applications such as recreational vehicles (RVs), boats, campers, and other vehicles with multiple batteries. They provide a simple and automatic way to manage the charging and isolation of batteries without the need for manual intervention.
One of the advantages of voltage-sensitive relays is their ease of installation and operation compared to more complex battery isolator systems. They are typically reliable and cost-effective solutions for maintaining the charge of auxiliary batteries while protecting the primary battery from excessive discharge.